Have you ever looked at a flight path on a map and wondered why airplanes take curved routes instead of flying in a straight line? Wouldn’t flying in a direct line be more fuel-efficient and faster? At first glance, it seems logical that a shorter distance would result in less fuel consumption, but in reality, aviation is far more complex.
Several factors determine flight paths, including the Earth’s shape, jet streams, weather conditions, and air traffic regulations. Let’s break down why airplanes rarely fly in a straight line and how their curved paths actually make flights more efficient.
The Earth’s Shape and the Great Circle Route

One of the biggest reasons airplanes don’t fly in a straight line is the Earth’s curvature. While we often view flight maps as flat, the Earth is a sphere, and the shortest path between two points is actually an arc called the Great Circle Route.
If you take a globe and use a string to connect two distant locations, you’ll notice that the shortest route often curves rather than follows a straight path. This is why flights from New York to Tokyo pass over the Arctic region rather than flying directly west across the Pacific Ocean.
Using the Great Circle Route helps planes save both time and fuel, even though it appears curved on a flat map.
Jet Streams and Weather Conditions Impact Flight Paths
Another key factor affecting airplane routes is jet streams—high-altitude wind currents that move at speeds of up to 200 mph (320 km/h). Pilots strategically plan routes to take advantage of these strong winds when possible.
Video : Why Airplanes Don’t Fly Straight
Flying with jet streams allows an airplane to get an extra push, helping it move faster while burning less fuel. Flying against a jet stream can slow down the plane significantly, increasing fuel consumption. Pilots often adjust routes to avoid strong headwinds, even if it means flying a longer distance.
Additionally, storms, turbulence, and severe weather conditions also play a role in determining flight paths. Airplanes may adjust mid-flight to bypass dangerous weather zones, thunderstorms, or areas with extreme turbulence.
Air Traffic Control and Flight Regulations
Air traffic isn’t a free-for-all where planes can just fly wherever they want. There are strict regulations set by aviation authorities and air traffic control (ATC) that dictate flight routes.
Some of these rules include restricted airspace, where certain areas, such as military zones, national security locations, and political zones, prohibit commercial flights from entering. Predefined flight corridors exist to avoid mid-air collisions, ensuring flights follow established air traffic lanes. Major airports handle hundreds of flights daily, so ATC ensures safe and efficient arrivals and departures.
Due to these regulations, airplanes cannot always take the most direct path and must follow designated routes instead.
Avoiding Air Turbulence for Passenger Comfort
Turbulence can make a flight uncomfortable, and pilots actively adjust routes to minimize rough air conditions. There are different types of turbulence, including thermal turbulence caused by warm air rising from the ground. Flying at higher altitudes helps avoid this.

Mechanical turbulence happens near mountains and rough terrains where wind patterns shift unpredictably. Clear-Air Turbulence (CAT) is sudden, strong air currents in high altitudes that are difficult to predict.
To ensure a smoother ride for passengers, pilots may deviate from the shortest path to avoid these turbulent areas.
Why Do Airplanes Sometimes Ascend Before Landing?
If you’ve ever been on a flight where the plane suddenly climbs just before landing, you might have felt a bit concerned. This maneuver is known as a go-around and is actually a common and safe aviation practice.
Some reasons why pilots perform a go-around include runway clearance issues. If another plane hasn’t cleared the runway in time, pilots must abort the landing and circle back. Poor weather conditions, such as poor visibility, strong crosswinds, or sudden gusts, can make a landing unsafe. If a plane is too fast, too high, or not properly aligned with the runway, the pilot will ascend and try again for a safer landing.
Go-arounds are standard procedures in aviation and ensure passenger safety above all else.
The World’s Longest Non-Stop Flight
While most flights follow curved paths, some routes push the limits of non-stop travel. The longest direct commercial flight in the world is from Singapore to Newark, New Jersey, USA.
This flight covers a distance of 10,400 miles (16,700 km) and takes approximately 18 hours and 45 minutes. It follows a carefully optimized path to balance fuel efficiency, wind conditions, and passenger comfort.
Video : Does Earth’s Rotation affect the Airplanes Speed & Flight Time
What Happens If a Plane Suddenly Loses Cabin Pressure?
A sudden drop in cabin pressure is often portrayed as a dramatic event in movies, but in reality, pilots are well-trained to handle it calmly.
When this happens, oxygen masks automatically deploy, and passengers should put them on immediately and breathe normally. The plane will descend to a safe altitude where oxygen levels are sufficient for breathing. The flight crew will assess the situation and communicate with passengers.
Losing cabin pressure doesn’t mean the plane will crash—pilots follow strict safety protocols to handle such incidents efficiently.
Final Thoughts: Why Curved Flight Paths Are More Efficient
While it may seem counterintuitive, airplanes take curved routes instead of straight lines to optimize flight efficiency, fuel usage, and passenger safety. Factors such as the Earth’s shape, jet streams, air traffic control, and weather conditions all play a crucial role in determining flight paths.
So next time you’re on a plane and see the route map displaying a curved flight path, remember there’s a lot of science and planning behind it to ensure you reach your destination as safely and efficiently as possible.
Tom Jones opens up about his marriage and love life after wife’s passing
After Linda’s death, Tom cancelled all his concerts and released a short statement:
Wife’s passing
“Surrounded by her husband and loved ones, she passed away peacefully,” the Sir Tom’s website wrote.
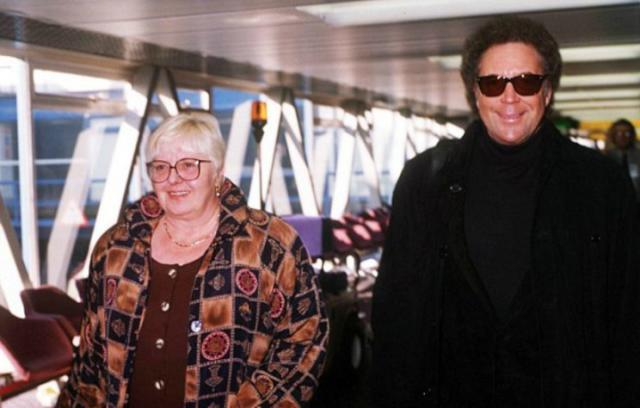

But last year, Sir Tom opened up on her tragic death. In an interview with This Morning, the Welshman said he would “never love again”.
His wife’s passing really crushed him and he struggled to perform on stage long after Linda was gone.
“When my wife passed away, I didn’t think I could sing,” Sir Tom explained. “When you’re emotional, you can’t sing, your voice closes up.
“There are certain songs I wouldn’t do. But you have to try and get things in the right perspective. Feeling emotional; use it to your advantage and put it into the song.
Now lives in London
“It took me a while,” he continued. “Took me a few months to try and see if I could sing. I got some of my musicians around and tried a few songs. But it was very emotional.”
Linda’s passing also had other consequences – Jones decided to sell their big mansion in Los Angeles, along with all their furniture, in order to move back to the UK.

Today he lives in a flat in London – that was Linda’s wish. His late wife had been homesick and wanted to move back to her roots, but cancer took her life before it was possible.
“She always said she wanted to come back and then she could not do it, so then she told me to do it in the last week she was alive,” said Sir Tom, who was married to Linda for 59 years.
There is no doubt that Jones still mourns Linda, whom he married at the age of 16. The couple met when Linda was 15.
Speaking to Radio 2, Sir Tom described the moment he first saw his wife-to-be:
“I remember her playing marbles and I thought, ‘My God, what great legs she’s got’. She was the best-looking girl around there and we got together. It was magic”, the singer said.

Linda and Sir Tom tied the knot as teenagers, just a month before their son, Mark, was born.
But their marriage would be rife with scandals and infidelity. For more than 50 years, Tom cheated on his wife.
om, who assumed the role of sex symbol, has previously admitted that he slept with 250 women a year at the peak of his career.
“From the very beginning, he was not exactly Mr Faithful,” biographer Sean Smith told Daily Mail in 2015.
It’s unclear how much Linda knew about her husband’s shady side, but it is clear that she suspected something wasn’t right. According to Sir Tom, the couple had a “don’t ask” policy when he was on tour.

”Linda lived a quiet life and rarely left the couple’s villa in Bel Air. During her single marriage to Tom, she has also had alcohol problems,” Robin Eggar, who wrote the official biography of Tom Jones, told the Daily Mail.
After 2003, the wife stopped accompanying her husband on his tours and remained mostly at home in the couple’s Bel Air mansion.

By then, she had already endured several scandals that must have tarnished their relationship.
In 1987, Tom Jones had a three-day fling with the 24-year-old Katherine Berkery, during tour in the US. According to reports, Katherine had no idea he was married and Tom refused to return her phone calls when she discovered she was pregnant with his child.
Nine months later, Jonathan Berkery was born in New York, in June 1988. Sir Tom denied he was Jon’s dad and refused to admit that it was his child.


Leave a Reply