
A few of us can still recall the days when “typing classes” required using real typewriters.
It is almost impossible to imagine that there was a period when typing had a tactile, almost rhythmic quality in an era when computerized screens rule our communication.
Our fingers danced across keys in a complete ten-finger ballet, not the constrained choreography meant for smartphones.
The medium for this dance was the typewriter, the mysterious device that ran on paper and ambition and required no electricity at all.

The late 1800s saw a great deal of advancement in communication technology, which is when the typewriter first came into being. Relics from this era are housed at the Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation, where curator Kristen Gallerneaux shows that the typewriter was not an immediate hit.
Its origins were largely due to Milwaukee printer Christopher Sholes and Carlos Glidden, who were inspired by a magazine article to design what would eventually become the first typewriter to be commercially successful.

The invention of Sholes and Glidden, who called it after themselves, was a technical miracle. It struck a compromise between the precision necessary for legible typing and the need for durability to withstand users’ need to “bang away on the keys.”
The typewriter took a while to become well-known despite its inventiveness; it didn’t take off until 1874.

The typewriter was a marvel of design as much as a technological achievement. The QWERTY keyboard layout, which was popularized by the Sholes and Glidden typewriter and is still in use today due to its efficiency in minimizing letter jamming by separating frequently used pairings, was introduced.
Centuries later, this keyboard layout’s answer to a mechanical issue unintentionally influenced how we use them.

The typewriter started to change the American workplace by the late 1880s. A notable change was brought about by the invention of the typewriter, which at first was used mostly by men.
By 1910, women accounted for nearly 80% of professional typists, a significant shift in the office setting.
This change was a social revolution that redefined gender roles in the workplace, not merely a technological one.

Innovations like the Nodin typewriter were the result of the search for a quieter typing experience. Its moniker, a witty reference to its silent functioning, perfectly captured the way typewriter design has continued to advance.
Even though the Nodin is a unique find, its presence demonstrates the inventive lengths inventors were willing to go to in order to enhance typing.

We haven’t even discussed electric typewriters in our history, which added a new level of convenience and noise to the typing experience. Nonetheless, early typewriters’ tactile feedback and straightforward mechanics have left a lasting impression on those who have used them.
Many individuals still enjoy listening to the old-fashioned clickity-clack sound of the keys.

The story takes a pleasant detour and returns to the act of typing. One of these old machines is available for you to type on, thanks to the curator at the Henry Ford Museum. The sensation serves as a sharp reminder of how physically demanding typing on a typewriter is, in sharp contrast to how natural typing on a modern keyboard is.
It’s a nostalgic moment that serves as a reminder of the development of writing technology and the timeless allure of typing.

The typewriter is a link to a lost era of communication because of its intricate mechanical design and lengthy history. It is a sentimental stroll down memory lane for those who recall. It’s an invitation to those who are unfamiliar with typing to discover the tactile delights of a world where words were created physically and each letter carried weight.
The typewriter is a monument to the human need for connection, communication, and creation even as we enter the digital age.
Watch the video below to find out more about the complex and fascinating history of the common typewriter! Kindly DISPLAY this to your loved ones.
62-year-old Billy Ray Cyrus marries 34-year-old bride Firerose – fans upset by one little detail
Billy Ray Cyrus recently celebrated his wedding to Firerose in an intimate ceremony. This union followed his divorce from Tish Cyrus in 2022, marking the third time they filed for divorce after 28 years of marriage. Following the divorce, Billy Ray Cyrus began dating Firerose, an Australian artist, and the two announced their engagement in November 2022.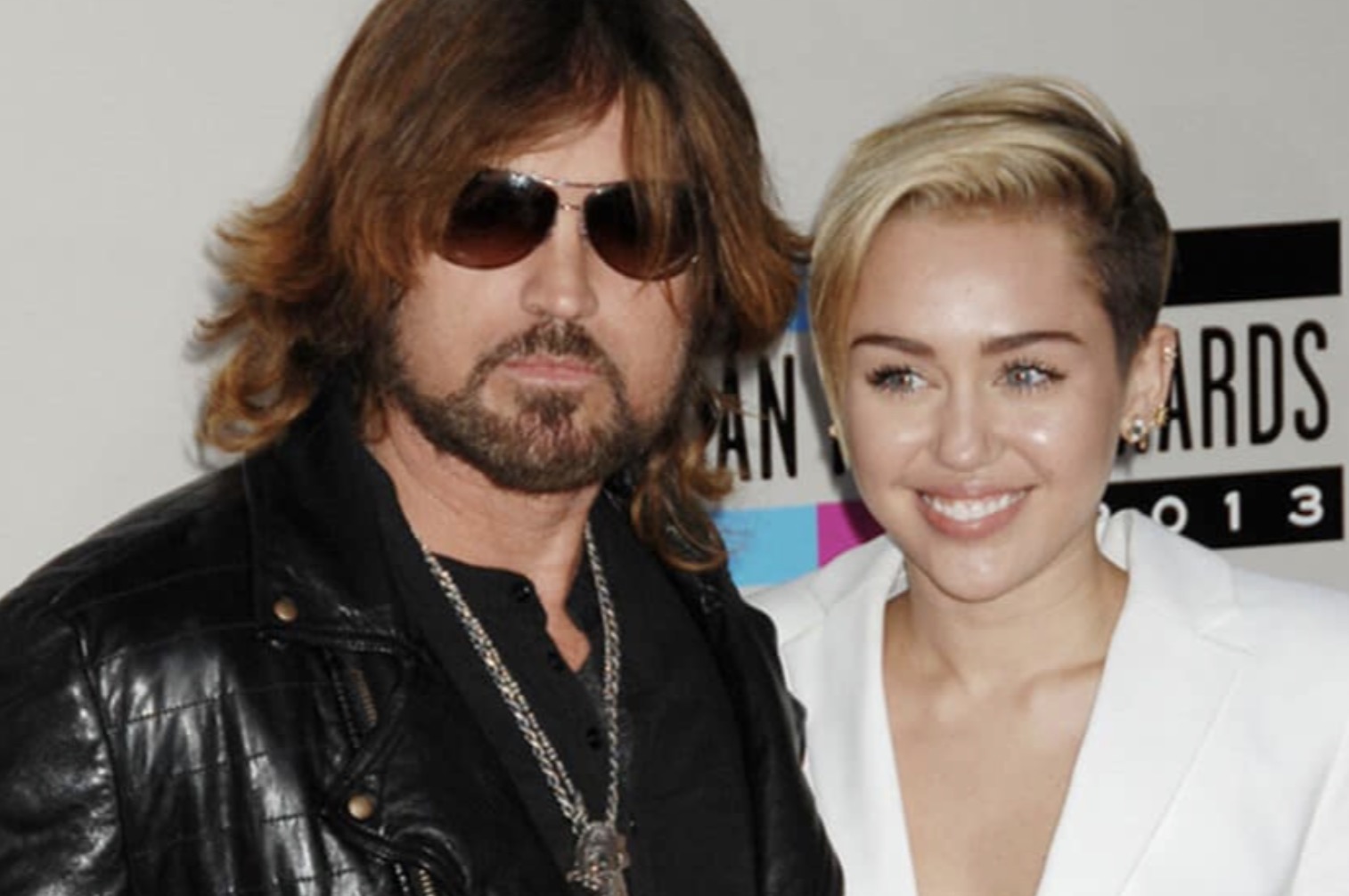 Interestingly, Billy Ray and Firerose had crossed paths years ago when Firerose auditioned for a role on “Hannah Montana” 13 years prior. This serendipitous encounter left a lasting impression on Billy Ray, who recalled the moment he first saw her and sensed her star potential. Although she didn’t land the role, Billy Ray introduced her to some producers, which ultimately led to a friendship that would later blossom into a romantic relationship.
Interestingly, Billy Ray and Firerose had crossed paths years ago when Firerose auditioned for a role on “Hannah Montana” 13 years prior. This serendipitous encounter left a lasting impression on Billy Ray, who recalled the moment he first saw her and sensed her star potential. Although she didn’t land the role, Billy Ray introduced her to some producers, which ultimately led to a friendship that would later blossom into a romantic relationship.
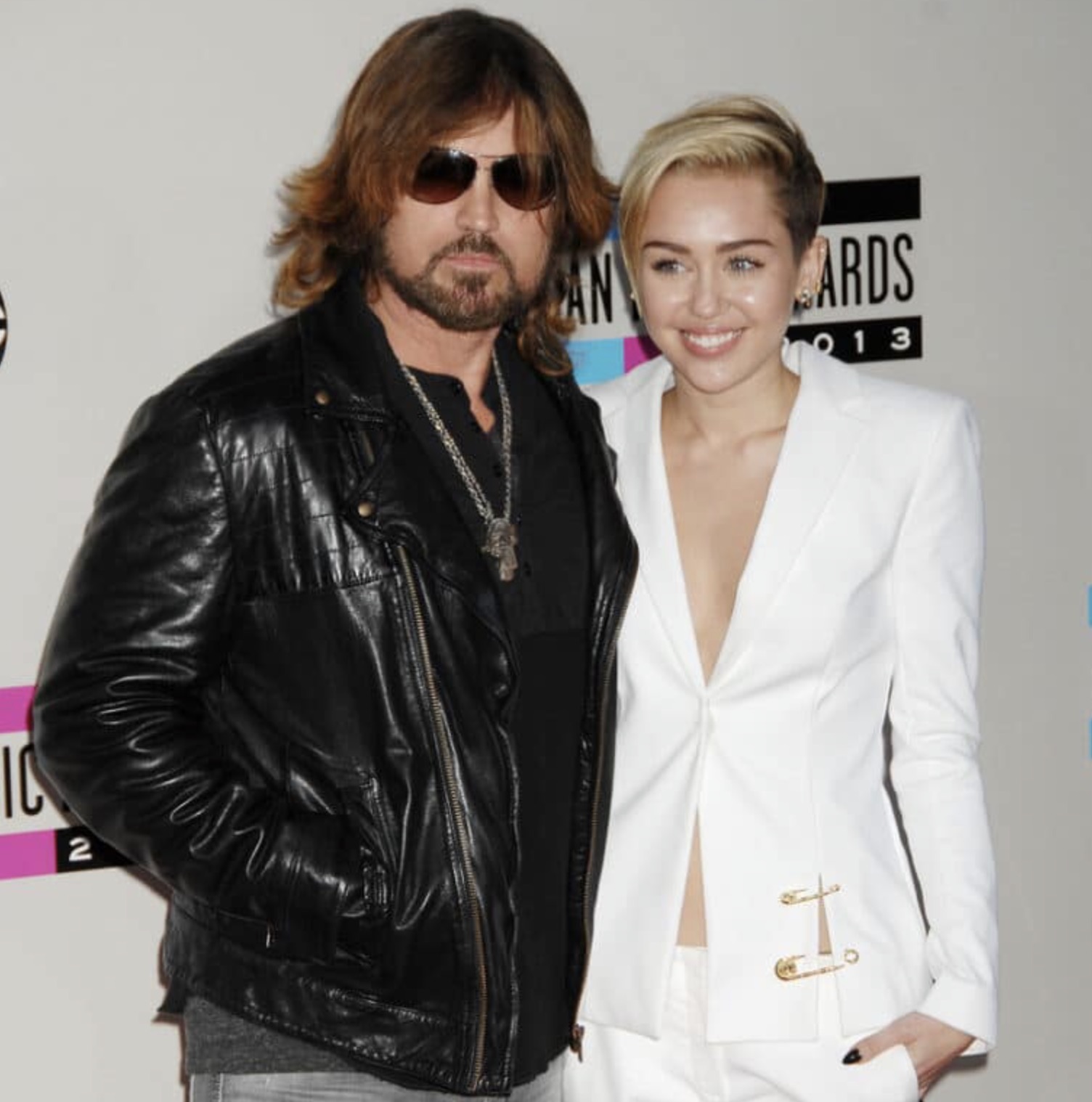

Billy Ray and Firerose’s love story developed after his divorce in early 2022. They officially became a couple, and Firerose moved in with him in August 2022. Shortly thereafter, he proposed, and they decided to make their love official through marriage.
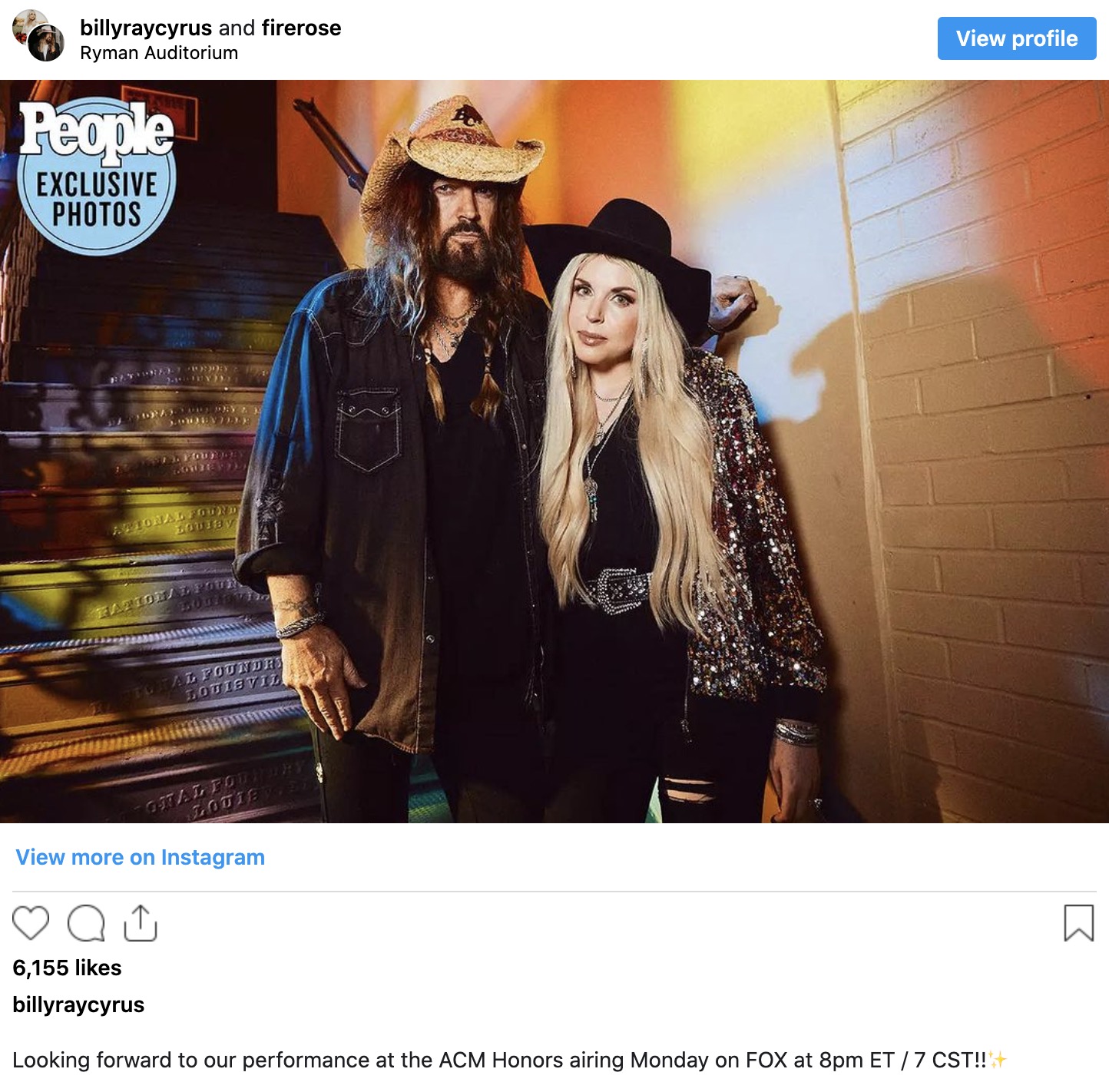
Their wedding coincided with Tish Cyrus, Billy Ray’s ex-wife, remarrying in August 2023 to “Prison Break” star Dominic Purcell. Tish’s two children from a previous relationship, Brandi and Trace, were in attendance at her wedding. Billy Ray had adopted Brandi and Trace while he was married to Tish. Billy Ray and Tish also have three children together: Miley Cyrus, Braison, and Noah.
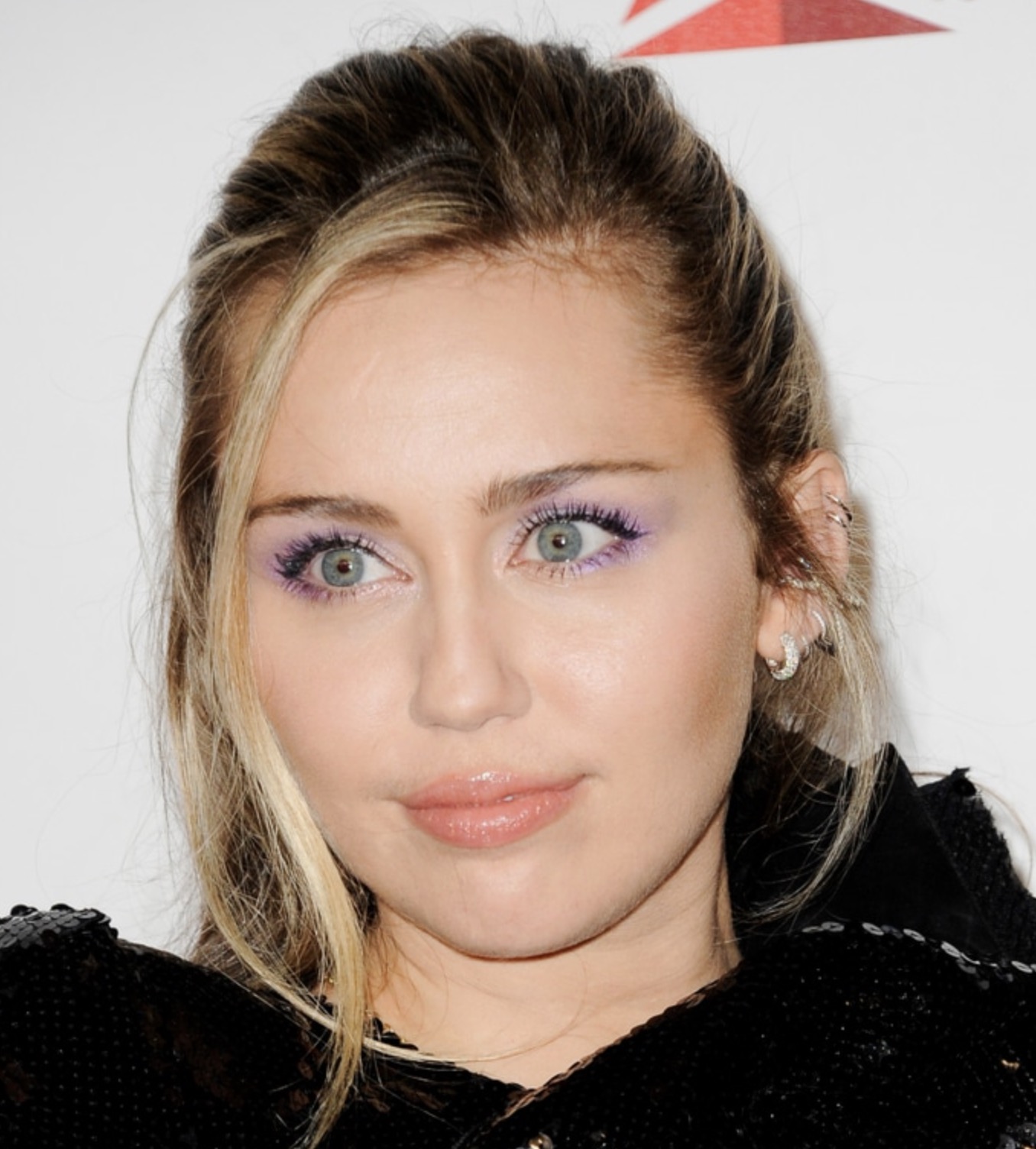

Notably, Noah and Braison were absent from their mother’s wedding. They were seen together on the day of the wedding, posting on Instagram about their outing to Walmart. The choice of their outing on the wedding day raised some eyebrows.
As Billy Ray and Firerose shared pictures from their wedding day on social media, some fans focused on one detail: Billy Ray Cyrus’s hair. Some fans expressed surprise and wondered why he didn’t style his hair differently for the occasion, with comments like, “Could have at least brushed his hair for the occasion” and “He couldn’t comb his hair??” This sparked discussion about his hairstyle choice for the wedding.
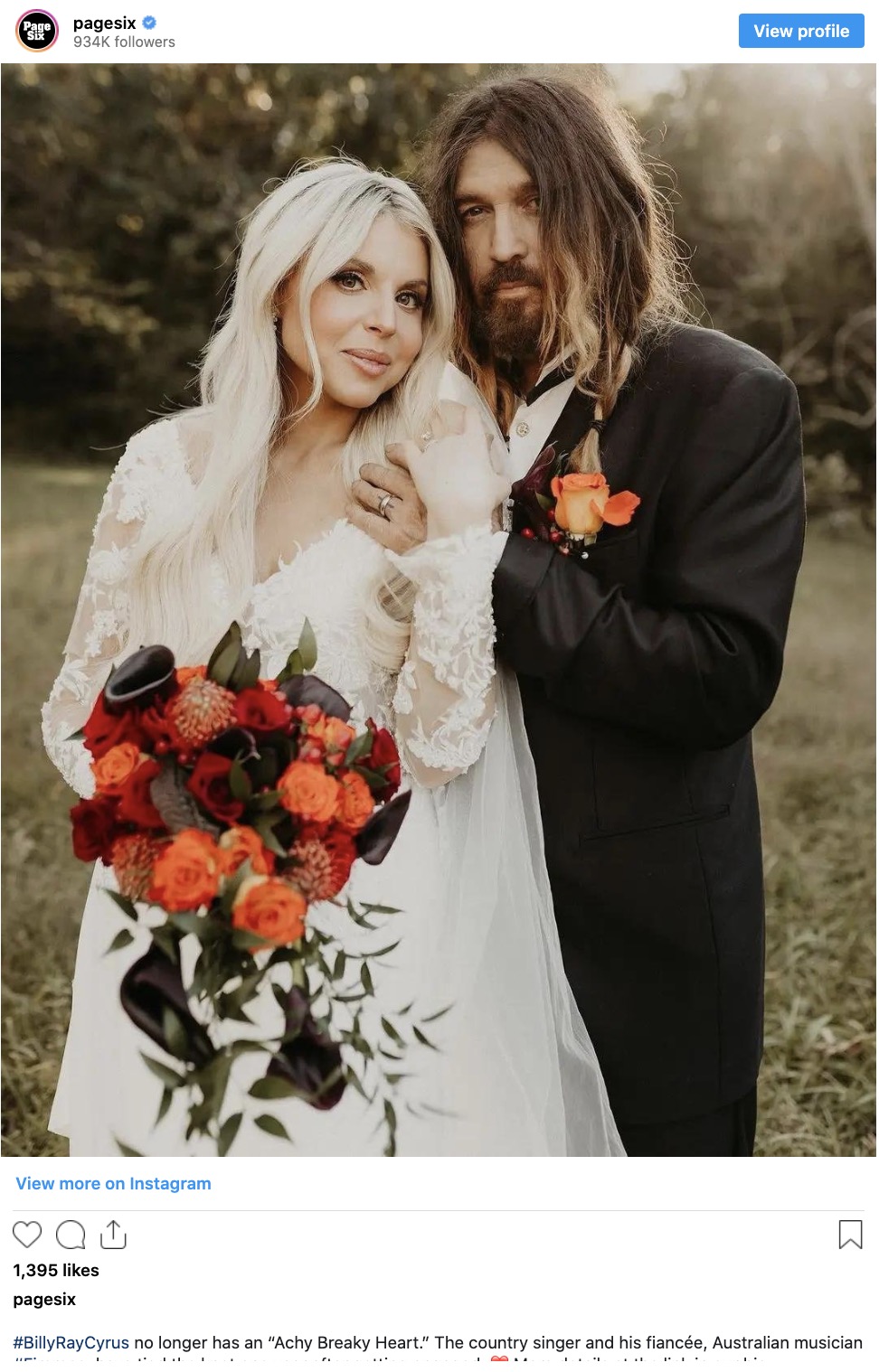

Billy Ray Cyrus and Firerose’s wedding marked a significant moment in their relationship, and while the focus may have been on his hair for some, it’s a celebration of love and happiness that they both clearly cherish.



Leave a Reply